Overweight
Scientific studies (review articles) on the relationship between diet/nutrients and overweight prevention:
One swallow does not make a summer. A famous Dutch saying that could not be any more obvious. Just because one single scientific study about a certain topic makes certain claims, it does not necessarily mean it is true. On the other hand, a review article (a collection of scientific studies on a certain topic) of randomized, placebo-controlled double blind clinical trials (RCTs) will answer the following question:
"Do taking dietary supplements make sense?" Yes for a positive conclusion and no for a negative conclusion.
One swallow does not make a summer. A famous Dutch saying that could not be any more obvious. Just because one single scientific study about a certain topic makes certain claims, it does not necessarily mean it is true. On the other hand, a review article (a collection of scientific studies on a certain topic) of cohort studies or case-control studies will answer the following question:
"Should I change my diet?".
2023:
2021:
- High protein diets causally have beneficial effect on body weight management
- High circulating vitamin C level reduces metabolic syndrome
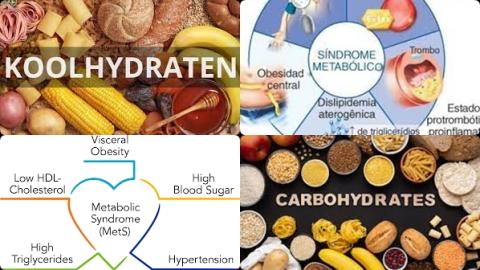
- Carbohydrate intake increases metabolic syndrome
- Poultry consumption decreases metabolic syndrome
- Nut consumption does not increase adiposity
- Obesity increases colorectal cancer in men with Lynch Syndrome
- A diet with low GI increases metabolic syndrome
- Hyperlipidemia, obesity and high alcohol consumption are risk factors of early-onset colorectal cancer
- Obesity is a risk factor for mortality from primary liver cancer
- Insufficiency of serum carotenoids increases overweight and obesity
- Obesity increases atrial fibrillation recurrence in patients undergoing catheter ablation
- Brown rice has anti-obesity effects in comparison with white rice
- No effect of vitamin E supplementation on weight, BMI and waist circumference
- Mortality is more frequently in COVID-19 patients with chronic kidney diseases and cardiovascular disease
- Vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy or infancy reduces adiposity in childhood
2020:
- Dairy products reduce causal fat mass and BMI among overweight or obese adults
- Pistachio supplementation lowers BMI without increasing body weight
- Abdominal adiposity is a risk factor in COVID-19
- Alpha-lipoic acid supplementation reduces weight and BMI
- Obesity increases severe COVID-19
- Coenzyme Q10 supplementation does not decrease body weight and BMI
- Yogurt intake is associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes
- Fish consumption reduces metabolic syndrome
- Waist circumference is a significant risk factor of liver cancer
2019:
- A higher serum copper level increases obesity
- 100 g/d fruit consumption reduces metabolic syndrome
- 150 mg/day quercetin supplementation reduces LDL-cholesterol in obese people
- <2 g/d L-carnitine decreases diastolic blood pressure in participants with obesity
- 280 mg/d dietary calcium intake may reduce metabolic syndrome
- Adults with overweight/obesity benefit from probiotics
- ≤400 μg/d chromium supplementation reduce BMI
- Whole grains, fruit, nut, legume consumption reduce adiposity risk
- Tree nuts reduce risk of metabolic syndrome
2018:
- ≥75 mg/day isoflavones reduce BMI
- <50 g/d carbohydrates increase good cholesterol in overweight/obese adults
- ≥30g chocolate per day during 4-8 weeks reduce BMI
- Carotenoids may reduce risk of metabolic syndrome
- Ginger intake reduces body weight and fasting glucose among overweight and obese subjects
- Vegetable and fruit consumption reduce metabolic syndrome
2017:
- A low-fat diet reduces cholesterol level in overweight or obese people
- A high dietary fiber intake may reduce risk of metabolic syndrome
- A high fruit and/or vegetable consumption reduce risk of metabolic syndrome among Asian
- A high relative adipose mass reduces bone mineral density in overweight and obese populations
- Higher sodium increases metabolic syndrome
- Metabolic syndrome increases risk of ischemic stroke
- A higher circulating DHA is associated with a lower metabolic syndrome risk
- Whole flaxseed supplementation in doses ≥30 g/d during ≥12 weeks has positive effects on body composition in overweight participants
- n-3 PUFA supplements reduce waist circumference in overweight and obese adults
- Green tea decreases LDL cholesterol level in overweight or obese people
- Decreased vitamin D levels and increased BMI increase pediatric-onset MS
- CLA does not reduce fasting blood glucose and waist circumference
- Abdominal adiposity and higher body fat mass increase risk of atrial fibrillation
2015:
XXXXXXXXXXX
Overweight is an increasing problem in the world. It’s called overweight when the BMI is greater than 25 and obese when the BMI is greater than 30. A healthy weight has a BMI of 18.5-25. A woman with 65 kg and 1.57 meters has a BMI of 26.4 (65/(1.57x1.57)). BMI is weight divided by height squared (weight (kg)/height2 (m)).
The best way to determine overweight in children is to calculate the BMI. In adults, beside the BMI, waist circumference should also be measured.
Everybody who wants to lose weight, wants to burn more calorie at rest and more fat. How do you achieve these two goals?
Make sure the resting metabolic rate (RMR) does not decrease when following a diet (therefore, the recommendation of dietitians is no more than 0.5-1 kg of weight loss per week). A low resting metabolic rate will result in a low calorie burning at rest. But that is not what you want. You want, when following a diet, that the body will burn more calories (at rest).
A low resting metabolic rate is often the result of the insufficient intake of carbohydrate. When the body obtains insufficient quantities of carbohydrate, it’s been forced to get energy from protein, resulting in muscle degradation. Muscle degradation will in turn result in a lower resting metabolic rate. Muscle degradation can be observed when the upper arm and calf circumference become smaller. To prevent muscle degradation, when following a diet, is recommendable to choose product with 55-70 En% carbohydrates.
To prevent muscle degradation when following a diet, the diet must contain at least 1.6 g protein per kg body weight. For a person of 65 kg means 65x1.6 = 104 kg of protein per day. 1.6 g protein per kg body weight corresponds to a diet with 20 En% protein.
To prevent muscle degradation when following a diet, it is recommendable to choose products with 20-35 En% protein and/or products with 55-70 En% carbohydrates in combination with strength training. Strength training increases the resting metabolic rate. A declined resting metabolic rate is often the cause of the yo-yo effect.
Cardio-fitness is a good way to burn fat. To be able to burn fat efficiently, you should perform cardio-fitness with the heart rate between 75 and 90% of the maximum heart rate. The maximum heart rate is calculated by 220 minus age.
For example, you are 40 years old you have to perform cardio-fitness with a heart rate between 0.75-0.9x(220-40) = 135 and 162 heart beats per minute. Stop immediately with the exercises when you are not feeling well or have pain in the chest!
In summary, it can be said the best way to lose weight is to perform strength training with cardio-fitness in combination with a diet containing products with 20-35 En% protein and/or products with 55-70 En% carbohydrates.
The main cause of overweight is the body gets more calories than it daily burns. Through physical activities, the body will burn more calories. To gain positive effects of physical exercises the body should burn at least 2000 calories (kcal) per week or at least 150 minutes of aerobic exercise of moderate intensity, accumulated over the week, which can be split into periods of at least 10 minutes. To prevent overweight, physical activities should account for 15-30% of the daily calorie intake.
The main consequences of overweight are:
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Type 2 diabetes. The main effects of type 2 diabetes are cardiovascular diseases and kidney problems.
Belly fat is bad because it increases the risk of getting type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Therefore, aim for a waist circumference of 68-80 cm for women and 79-94 cm for men. A loss of 1 cm of belly fat (e.g. 95 to 94 cm) corresponds to a loss of 1 kg of fat. 1 kg of fat corresponds to 9000 calories.
Local fat loss, such as the backside or thighs is a scientific myth.
The human body will only burn fat when it meets the following two criteria:
- Increased oxygen uptake (only occurs during physical exercises).
- Increased energy demand (only occurs during physical exercises).
We like to eat fat but our body likes to use carbohydrates as energy source.
Overweight is the result of poor knowledge about nutrition in combination with hardly physical exercises.
It is not possible to lose more than 1.8 grams of fat per week. However, at more than 1 kg of fat loss per week, the body will also break down muscle, resulting in a low resting metabolic rate and yoyo-effect.
When following a diet is favorable to minimize fat through diet. But at least 7 grams of fat per day is necessary to ensure the intake of essential fatty acids and to stimulate the production of bile salts.
7 grams of fat per day corresponds to a daily diet with 4 En% fat. However, a diet with at least 20 En% fat (and up to 35 En% fat) is necessary to prevent a deficiency of essential fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins on long-term.
A responsible breakfast contains up to 350 kcal.
A responsible lunch contains up to 450 kcal.
A responsible evening meal contains up to 750 kcal.
Good indicators for weight loss are a decreased body fat and an increased muscle mass. The body fat and muscle mass can be measured with a body composition analyzers scale.
| Recommended daily energy intake by sex and age group | ||
| Age group (years) | Men | Women |
| Kcal per day | Kcal per day | |
| 6 | 1600 | 1500 |
| 12 | 2200 | 2000 |
| 17 | 2900 | 2300 |
| 30-39 | 2600 | 2000 |
| 50-59 | 2500 | 2000 |
| 70-79 | 2300 | 1800 |
| Others | 2500 | 2000 |
| Recommended fat percentage by sex and age group | ||
| Age group (years) | Men | Women |
| 17-29 | 15 | 25 |
| 30-39 | 17.5 | 27.5 |
| 40-49 | 20 | 30 |
| 50+ | 25 | 35 |
| A healthy adult male has a body fat percentage around 15%. A healthy adult woman has a body fat percentage around 25%. | ||
Dietary guidelines for overweight prevention:
- Choose products with 20-30 En% fat, products with maximum 7 En% saturated fat, products with 20-35% protein, products with maximum 10 En% sugars, products with minimum 1.5 grams of fiber per 100 kcal and products with a GI value of 55 or lower or in other words, your daily diet (=all meals/products that you eat on a daily basis) should on average contain 20-30 En% fat, maximum 7 En% saturated fat, 20-35% protein, maximum 10 En% sugars and minimum 1.5 grams of fiber per 100 kcal.
- Products with 20-35 En% protein in combination with 10000 steps per day and 25-30 grams of fiber per day will reduce weight in a responsible manner.
Products with 20-35 En% protein should contain maximum 30 En% fat and maximum 7 En% saturated fat! - No more than 0.5-1 kg of weight loss per week. 0.5 kg of weight loss per week corresponds to a decreased intake of 350 kcal per day through diet and 150 kcal extra through physical activities.
- To prevent a deficiency of vitamins and essential fatty acids a diet should contain a minimum of 1700 kcal per day.
- Increase the resting metabolic rate. Strength training is the best way to increase the resting metabolic rate.
- Use the following guideline: total energy intake per day is 25-30 kcal per kg body weight.
- Eat 300 grams of vegetables and five servings of fruit per day or 25-30 grams of fiber per day. Dietary fiber provides a longer satiety, resulting in less meal times during the day. Furthermore, the antioxidants from fruits and vegetables reduce inflammation.
30 grams of fiber per day corresponds to a daily diet of minimum 1.5 grams of fiber per 100 kcal. - Eat no more than 19 grams of saturated fat per day at 2500 kcal and 15 grams of saturated fat at 2000 kcal. The WHO advises 2000 kcal per day for women and 2500 kcal for men.
- Aim for a healthy weight. A healthy weight has a BMI of 18.5-25. BMI is weight divided by height squared (weight (kg)/height2 (m)).
- Spend at least 90 minutes per day on physical exercises or at least 10000 steps per day.
- Stop smoking because smoking causes atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the most important cause of cardiovascular diseases.
- Do not go shopping on an empty stomach.
- Do not skip breakfast.
- Put the meal on a small plate. So it looks like there is a lot of food on the plate!
- Eat at least 2 times (100-150 g fish per time) a week oily fishes or take daily 250-500 mg EPA and DHA.
Oily fishes are sardines, herring, salmon, anchovies, eel and mackerel. - Limit alcohol to 2 glasses for men and 1 glass for women per day.
- Eat no more than 6 grams of salt per day, corresponding to 2400 mg of sodium.
6 grams salt per day corresponds to a daily diet with <0.3 g salt per 100 kcal. - Do not take weight loss supplements. They do not what they claim.
| Age (years) | Recommended BMI for men | Recommended BMI for women |
| 4 | 14.40-17.55 | 14.25-17.28 |
| 5 | 14.20-17.42 | 14.05-17.15 |
| 6 | 14.04-17.55 | 13.90-17.34 |
| 7 | 14.02-17.92 | 13.94-17.75 |
| 8 | 14.10-18.44 | 14.06-18.35 |
| 9 | 14.29-19.10 | 14.26-19.07 |
| 10 | 14.53-19.84 | 14.57-19.86 |
| 11 | 14.84-20.55 | 14.99-20.74 |
| 12 | 15.23-21.22 | 15.52-21.68 |
| 13 | 15.70-21.91 | 16.13-22.58 |
| 14 | 16.25-22.62 | 16.73-23.34 |
| 15 | 16.84-23.29 | 17.28-23.94 |
| 16 | 17.42-23.90 | 17.75-24.37 |
| 17 | 17.98-24.46 | 18.16-24.70 |
| 18 and older | 18-50-25.00 | 18.50-25.00 |