Cardiovascular diseases
Scientific studies (review articles) on the relationship between diet/nutrients and cardiovascular diseases:
One swallow does not make a summer. A famous Dutch saying that could not be any more obvious. Just because one single scientific study about a certain topic makes certain claims, it does not necessarily mean it is true. On the other hand, a review article (a collection of scientific studies on a certain topic) of randomized, placebo-controlled double blind clinical trials (RCTs) will answer the following question:
"Do taking dietary supplements make sense?" Yes for a positive conclusion and no for a negative conclusion.
One swallow does not make a summer. A famous Dutch saying that could not be any more obvious. Just because one single scientific study about a certain topic makes certain claims, it does not necessarily mean it is true. On the other hand, a review article (a collection of scientific studies on a certain topic) of cohort studies or case-control studies will answer the following question:
"Should I change my diet?".
2023:
- 500 mL/d orange juice consumption causally reduce bad cholesterol
- 30g/d whole grains consumption reduce all-cause mortality
- Dietary intake of 200-700 mg/day calcium reduces stroke among Asians
- Green tea may causally improve risk factors of cardiovascular disease
- Green tea causally lowers blood pressure in healthy individuals
2022:
- 20 g/day olive oil reduce all-cause mortality
- 25-200 g/d peanuts may causally reduce total cholesterol levels
- Brassica vegetables causally reduce total cholesterol
- Higher dietary fiber intake improves causally cardiovascular risk factors
- 500 mg/d dietary flavonoid intake reduces cardiovascular disease, diabetes and hypertension
- Serum vitamin D concentrations between 40 and 75 nmol/L reduce hypertension in adult
- 200 mg/day flavan-3-ols dietary intake reduce stroke
- Dietary oat supplementation may improve BMI among obese participants with mild metabolic disturbances
2021:
- Purified anthocyanin supplements reduce cardiovascular risk
- HDL cholesterol level under 2.33 mmol/L reduces cardiovascular disease mortality
- Higher sodium and lower potassium reduce in a dose-response manner cardiovascular risk
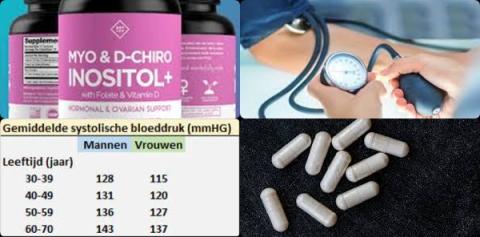
- 4000 mg inositol supplements reduce blood pressure
- 25 mg/d dietary flavonols or 5 mg/d dietary flavones reduce coronary heart disease
- Low-carbohydrate diets decrease LDL particle number
- Onion causally increases good cholesterol
- Dyslipidemia increases severity and mortality of COVID-19
- Best cut-off point of homocysteine for predicting acute ischemic stroke is 20.0 μmol/L
- Green leafy vegetables reduce cardiovascular disease
- Clinical screening for blood pressure in cerebral palsy is needed
- White meat reduces all-cause mortality
- Obesity increases atrial fibrillation recurrence in patients undergoing catheter ablation
- Cardiovascular drugs may not be associated with poor COVID-19 outcomes
- Low to moderate alcohol intake decreases venous thromboembolism
- Rice bran oil causally decreases cholesterol and triglyceride levels in adults
- Most prevalent neurological comorbidity in COVID-19 is cerebrovascular disease
- Weekly 175-350 grams oily fish lower cardiovascular disease among patients with vascular disease
- Mortality is more frequently in COVID-19 patients with chronic kidney diseases and cardiovascular disease
- Soy consumption causally lowers blood pressure in adults
- Daily 700-1000 mg dietary calcium intake increases cardiovascular disease in healthy postmenopausal women
- High NT-pro BNP and CK-MB levels in COVID-19 patients correlate with worse outcomes
- Diet with <30 En% carbohydrates causally increases adiponectin concentration in adults
- Omega-3 fatty acids consumption reduce recurrent venous thromboembolism
2020:
- 1-mg/day dietary heme iron intake increase cardiovascular disease mortality
- <3 cups/d coffee is essential for the prevention of dyslipidemia
- Higher intakes of total protein reduce all-cause mortality
- 2-3 servings/week fish reduce all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Every 1 gram sodium increases cardiovascular disease risk by 6%
- Most prevalent comorbidities among COVID-19 are hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, liver disease, lung disease, malignancy, cerebrovascular disease, COPD and asthma
- A higher fish consumption reduces coronary heart disease
- Dietary intake of vitamin B6 and folate reduces stroke
- A high serum vitamin C reduces blood pressure
- Male, age, cardiovascular disease, hypertension and diabetes mellitus increase mortality in patients with COVID-19
- Green tea reduces blood pressure in subjects with hypertension
- Potassium intake from 3,128 mg per day increases blood pressure
- Tomato consumption reduces bad cholesterol levels
- 200-1500 mg/d dietary calcium intakes do not increase cardiovascular disease
- 1-3 eggs/day during 3 to 12 weeks have no effect on blood pressure
- 100 mg/day magnesium dietary intake reduce type 2 diabetes
- Alzheimer disease increases risk of hemorrhagic stroke
- Pneumococcal vaccination may decrease all-cause mortality in patients with cardiovascular disease
- 100-g/d fish consumption decreases liver cancer
- Yogurt intake is associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes
- Daily 1 cup tea decreases all-cause mortality among elderly
- Hypertension, diabetes, COPD, cardiovascular disease and cerebrovascular disease are major risk factors for patients with COVID-19
- Hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, smoking, COPD, malignancy and chronic kidney disease are risk factors for COVID-19 infection
- Flaxseed supplementation decreases plasma lipoprotein(a) levels
- Higher linoleic acid blood concentration reduces cancer mortality
- Cardiovascular metabolic diseases increase risk of corona virus infection
- Vitamin C supplements during ≥6 weeks reduce blood pressure
- Quercetin supplements decrease triglycerides levels
- Heart failure increases risk of all-cause dementia
- Low-carbohydrate diet reduces cardiovascular disease
2019:
- Grape products reduce bad cholesterol in adults
- <400 mg coffee bean extract supplementation reduces blood pressure in hypertensive patients
- Higher circulating concentration of vitamin C, vitamin E and β-carotene reduce cardiovascular mortality
- Saturated fat increases Alzheimer disease
- Dietary intakes of anthocyanins reduce hypertension
- Cashew consumption improves triglyceride levels
- Coenzyme Q10 supplements reduce inflammation in patients with coronary artery disease
- Kiwifruit does not improve cardiovascular risk factors
- Trans fatty acids intake increases cardiovascular disease
- Diet with high total antioxidant capacity decreases cancer mortality
- Peanut consumption more than 12 weeks increases good cholesterol
2018:
- High dietary vitamin E intake reduces risk of stroke
- Diet with medium-chain saturated fatty acids leads to higher HDL cholesterol
- 150 g/day French-fries consumption increases risk of hypertension
- 10,000 steps a day do not decrease blood pressure in healthy adults
- Walnut-enriched diet reduces cholesterol and triglyceride levels
- Higher sodium intake and higher dietary sodium-to-potassium ratio are associated with a higher risk of stroke
- EPA/DHA ratio of < 1 reduces risk of postoperative atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass grafting
- Coronary heart disease and heart failure increase risk of dementia
- Coenzyme Q10 supplementation reduces serum triglycerides levels of patients with metabolic disorders
- Olive oil consumption decreases LDL cholesterol and triglyceride less than other plant oils
- 1 serving/week poultry intake reduces risk of stroke among US people
- Resveratrol supplements do not reduce LDL-cholesterol levels
- 20g/d of fish consumption reduce risk of CVD mortality
2017:
- Replacing saturated fat with PUFA will lower coronary heart disease events
- Omega-3 supplementation decreases risk of cardiac death
- 500 mL/d beetroot juice reduces blood pressure
- Atrial fibrillation, previous stroke, myocardial infarction, hypertension, diabetes and previous TIA increase risk of post-stroke dementia
- Daily dietary intake of 30g whole grains, 100g fruits and 200g dairy products reduce risk of hypertension
- At least 28 g/d whole grain intake reduce risk of total, cardiovascular and cancer mortality
- Red and processed meat increase risk of stroke
- 8.7 g/day viscous soluble fiber during 7 weeks reduces blood pressure
- A diet with <10 En% saturated fat reduces cholesterol and blood pressure in children
- Consumption of whole grains, fish, vegetables and fruit decrease risk of cardiovascular diseases
- Coenzyme Q10 supplements result in lower mortality and improved exercise capacity of patients with heart failure
- EPA and DHA supplements reduce risk of cardiovascular diseases
- Up to 12g/day nut consumption is associated with reduced all-cause and coronary heart disease mortality
- 1-724 mg/day anthocyanin supplementation improve vascular health
- Weekly 30-180 gram chocolate consumption reduces risk of coronary heart disease, stroke and diabetes
- Resistance training reduces blood pressure in prehypertensive and hypertensive subjects
- Perioperative antioxidant vitamin therapy in patients undergoing cardiac surgery reduces the incidence of postoperative atrial fibrillation and duration of hospital stay
- No association between dietary choline/betaine with incident cardiovascular disease
- 0.1-7 drinks/week reduce risk of heart failure
- 100-mg/day flavonoids decrease risk of all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality
- Potassium supplementation for at least 4 weeks reduces blood pressure of patients with essential hypertension
- 100 mg/day dietary magnesium intake is associated with lower risk of hypertension
- Daily 1 egg increases heart failure risk
- A daily dose of ≥200 g yogurt intake decreases cardiovascular disease risk
- Sesame consumption reduces systolic blood pressure
- Higher lycopene exposure reduces risk of cardiovascular diseases
- Abdominal adiposity and higher body fat mass increase risk of atrial fibrillation
- Tomatoes reduce cardiovascular risk among adults
2016:
- Elevated serum phosphorus concentration increases risk of all-cause mortality among men without chronic kidney disease
- Garlic supplementation reduces cardiovascular disease risk
2015:
- Vitamin B1 deficiency increases systolic heart failure risk
- A high GL diet is a risk factor of stroke events
2014:
- Olive oil consumption reduces stroke
- Perioperative antioxidant supplementations with NAC, PUFA and vitamin C prevent atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery
2013:
2012:
- A low GI diet decreases LDL-cholesterol
- Flavonoid supplements show significant improvements in vascular function and blood pressure
2011:
2002:
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
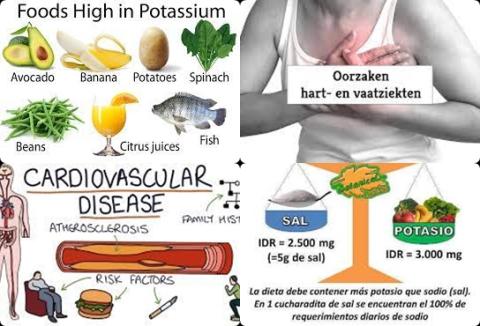
Cardiovascular disease is a class of diseases that involves the heart or blood vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins). Cardiovascular diseases are TIA, heart attack, stroke and vascular disease of the large vessels, such as claudication. Cardiovascular diseases are currently number 1 cause of death in the Western world.
The main causes of cardiovascular diseases are:
- Arteriosclerosis (a thickening and hardening of arteries)
- Type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- High homocysteine levels
- Obesity
Rules of thumb:
- % reduction of cholesterol = % risk reduction of cardiovascular disease.
- Per kg weight loss = 1 mmHg blood pressure reduction. So from 130 to 120 mmHg would practically mean 10 kg weight loss.
- Each gram of salt above 6 grams of salt per day will increase the blood pressure by 1 mmHg.
Daily intake of 3 grams of plant sterols or stanols during 2-3 weeks reduces the LDL cholesterol level by 11.3%. However, avoiding dietary cholesterol is not the solution to a high cholesterol level. The solution is to choose products with maximum 30 En% fat, and maximum 7 En% saturated fat.
It is very difficult to decrease the cholesterol level by 15% by diet only.
A cholesterol lowering diet contains:
- Products with maximum 30 En%
- Products with maximum 7 En% saturated fat
- Products with maximum 15 En% protein
- Up to 200 grams of cholesterol per day
- Products with at least 1.5 grams of fiber per 100 kcal
Heredity also plays a role in cardiovascular diseases. The inherited forms of cardiovascular disease are:
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (=a heart disease in which the heart muscle is thickened)
- Dilated cardiomyopathy (=a heart disease in which the heart muscle is dilated)
- Long-QT syndrome
- Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT)
- Brugada syndrome
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD)
- Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH)
Symptoms of myocardial infarction in men and women are not the same.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction in men are chest pressure, sweating and pain radiating to the arms and jaw.
Symptoms that may indicate a heart attack in women are:
- Palpitations (pounding heart)
- Sudden dizziness, a feeling of weakness
- Insomnia
- An uncomfortable feeling in the stomach, possibly with nausea
- A sudden onset of extreme fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Burning sensation below the sternum
- Unpleasant clamping or tightness in the chest
- Unpleasant sensation or pain between the shoulder blades, pain in the neck
Dietary guidelines for cardiovascular disease prevention:
- Choose products with maximum 30 En% fat, products with maximum 7 En% saturated fat, products with maximum 0.3 gram salt per 100 kcal, products with minimum 1.5 grams of fiber per 100 kcal and for fish which provides at least 1000 mg of EPA and DHA per day or in other words, your daily diet (=all meals/products that you eat on a daily basis on average) should contain maximum 30 En% fat, of which maximum 7 En% saturated fat, maximum 0.3 gram salt per 100 kcal and minimum 1.5 grams of fiber per 100 kcal.
- Stop smoking because smoking causes atherosclerosis.
- Aim for a healthy weight. A healthy weight has a BMI of 18.5-25. BMI is weight divided by height squared (weight (kg)/height2 (m)).
- Spend at least 60-90 minutes of physical exercises per day or at least 10000 steps per day.
- Eat at least 2 times (100-150 g fish per time) a week oily fish. Oily fishes are sardines, herring, salmon, anchovies, eel and mackerel.
- Eat 250 mg omega-3 fatty acids per day. Omega-3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid, EPA and DHA.
- Eat 300 grams of vegetables and five servings of fruit per day or 30 grams of fiber per day.
30 grams of fiber per dag corresponds to a daily diet of minimum 1.5 grams of fiber per 100 kcal.
10 to 30 grams of fiber a day decreases the LDL cholesterol levels. - Eat plenty of whole grains (brown bread, brown rice and oats) and legumes.
- Limit alcohol consumption to 2 glasses for men and 1 glass for women per day.
- Eat no more than 6 grams of salt per day, corresponding to 2400 mg of sodium.
- Eat no more than 200 grams of cholesterol per day at an elevated LDL-cholesterol level.
- Eat no more than 19 grams of saturated fat per day at 2500 calories diet and 15 grams of saturated fat at 2000 kcal diet. The WHO advises 2000 kcal per day for women and 2500 kcal for men.
- Take 500 micrograms of folic acid per day at a high homocysteine level.
- Do not take antioxidant supplements. They do more harm than good!
Consult your doctor or a dietician when taking dietary supplements!
| Target values for a healthy heart: | |
| Measurement | Reference values |
| Total cholesterol level | < 4.5 mmol/l |
| HDL cholesterol level for men | > 0.9 mmol/l |
| HDL cholesterol level for women | > 1.1 mmol/l |
| LDL cholesterol level | < 2.5 mmol/l |
| Triglycerides (blood fats) level | < 2.5 mmol/l |
| Fasting blood sugar level | < 6 mmol/l |
| HbA1c | < 7% |
| Homocysteine level | < 12 micromol/l |
| Blood pressure | 120/80 mmHg. 120 is systolic blood pressure & 80 is diastolic blood pressure |
| Blood pressure in people over 60 years | 140/90 mmHg |
| Lifestyle measures for the treatment and prevention of high blood pressure | ||
| Lifestyle changes | Recommendation | Reduction of systolic blood pressure |
| Weight loss | A healthy weight has a BMI of 18.5-25 kg/m2 | 5-20 mmHg |
| Salt reduction | Up to 6 grams of salt a day or 2400 mg of sodium per day | 2-8 mmHg |
| Potassium intake | Per every increment of 0.6 gram | 1 mmHg |
| Physical activities | 30-60 minutes of physical activity per day | 4-9 mmHg |
| Alcohol consumption | Maximum 2 glasses for men & 1 glass for women | 2-4 mmHg |
| DASH diet | Nutritional pattern rich in fruits, vegetables and low-fat products | 8-14 mmHg |
| This table shows that the best way to prevent high blood pressure is to maintain a healthy weight | ||