20 mg/d isoflavones dieatary intake reduces risk of colorectal neoplasms in Asians

Objectives:
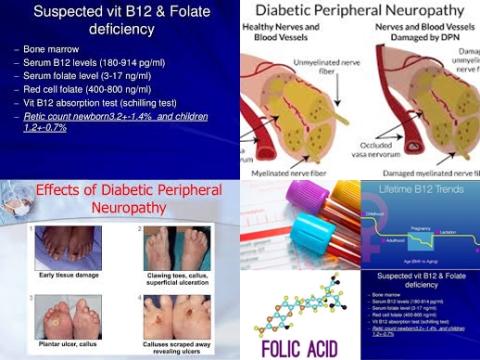
The association between serum folate and vitamin B12 levels and the risk of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) remains unclear. Therefore, this review article (meta-analysis) has been conducted.
Do reduced serum levels of folate and vitamin B12 increase peripheral neuropathy risk among patients with type 2 diabetes?
Study design:
This review article included 16 studies of serum folate levels (1190 patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy and 1501 patients without diabetic peripheral neuropathy) and 18 studies of serum vitamin B12 levels (1239 patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy and 1562 patients without diabetic peripheral neuropathy) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found reduced serum levels of folate in patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic peripheral neuropathy compared with patients with type 2 diabetes but without diabetic peripheral neuropathy [WMD = -1.64, 95% CI = -2.46 to -0.81].
A subgroup analysis confirmed this association in the Chinese population, but not in the Caucasian and mixed populations.
The investigators found reduced serum levels of vitamin B12 in patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic peripheral neuropathy compared with patients with type 2 diabetes but without diabetic peripheral neuropathy [WMD = -70.86, 95% CI = -101.55 to -40.17].
A subgroup analysis confirmed this association in the Chinese population, but not in the Caucasian and mixed populations.
The investigators concluded reduced serum levels of folate and vitamin B12 increase peripheral neuropathy risk among patients with type 2 diabetes. These findings support the need for further controlled studies in defined patient populations and the importance of monitoring serum folate and vitamin B12 levels in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Original title:
Serum folate, vitamin B12 levels and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis by Wang D, Zhai JX and Liu DW.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28081987
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on diabetes, folate and vitamin B12 right here.
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy is a long-term complication of diabetes. Exposure to high blood glucose levels over an extended period of time causes damage to the peripheral nerves; the nerves that go to the arms, hands, legs and feet. It is one of many complications associated with diabetes, with nearly 60 percent of diabetics having some form of nerve damage.
Objectives:
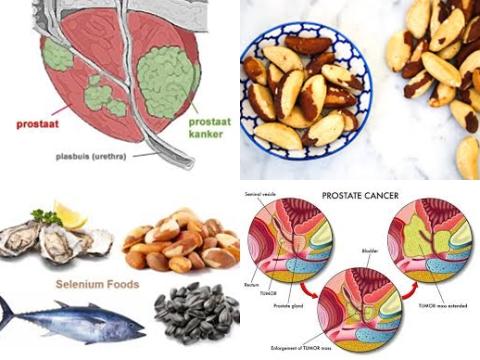
Some observational studies have shown that elevated serum selenium levels are associated with reduced prostate cancer risk. However, not all published studies support these results. Therefore, this review article (meta-analysis) has been conducted.
Does an elevated serum selenium level reduce prostate cancer risk?
Study design:
This review article included 12 case-control studies, 4 cohort studies and 1 RCT with 6,136 prostate cancer cases among 34,901 participants.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found elevated serum selenium levels significantly decreased prostate cancer risk with 24% [pooled OR = 0.76, 95% CI = 0.64 to 0.91, I2 = 60.8%, p = 0.001]. Significant means that there is an association with a 95% confidence.
The investigators found in subgroup analysis, an inverse association between elevated serum selenium levels and prostate cancer risk in case-control studies, current and former smokers, high-grade cancer cases, advanced cancer cases and different populations. However, such correlations were not found among cohort studies, nonsmokers, low-grade cancer cases and early stage cancer cases.
The investigators concluded that elevated serum selenium levels may decrease high-grade prostate cancer among current and former smokers. May decrease because the inverse relationship between elevated serum selenium levels and prostate cancer risk was not significant among cohort studies. Therefore, further cohort studies and randomized control trials based on non-Western populations are required.
Original title:
Serum selenium levels and prostate cancer risk: A MOOSE-compliant meta-analysis by Cui Z, Liu D, […], Liu G.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5293444/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on selenium and cancer right here.

Objectives:
Is there an association between individual micronutrients and blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes?
Study design:
This review article included 11 RCTs (13 interventions, 723 patients with type 2 diabetes and ages ranging from 50.7 to 66.8 years and 54% of them were males. The duration of diabetes varied from 4.6 to 8.6 years) with 3 to 52 weeks of follow-up were classified according to the type of micronutrient intervention: sodium (n = 1), vitamin C (n = 2), vitamin D (n = 7) and magnesium (n = 1).
Only a meta-analysis of vitamin C and D was able to perform with the available data.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found vitamin C significantly reduced diastolic blood pressure of patients with type 2 diabetes with 2.88mmHg [WMD = -2.88 mmHg, 95% CI = -5.31 to -0.46, p = 0.020].
However, vitamin C not significantly reduced systolic blood pressure [WMD = -3.93mmHg, 95% CI = -14.78 to 6.92, p = 0.478].
Significant means that there is an association with a 95% confidence.
The investigators found vitamin D significantly reduced diastolic blood pressure of patients with type 2 diabetes with 2.44mmHg [WMD = -2.44 mmHg, 95% CI = -3.49 to -1.39, p 0.001].
The investigators found vitamin D significantly reduced systolic blood pressure of patients with type 2 diabetes with 4.56mmHg [WMD = -4.56 mmHg, 95% CI = -7.65 to -1.47, p = 0.004].
The investigators concluded vitamin D and possibly vitamin C have beneficial effects on blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes. Therefore, these interventions might represent a novel approach to the treatment of hypertension in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Original title:
Effects of individual micronutrients on blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials by de Paula TP, Kramer CK, [...], Azevedo MJ.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5233957/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on diabetes and vitamin C and D right here.
Objectives:
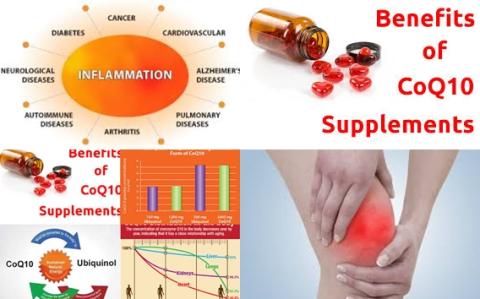
Has coenzyme Q10 supplementation lowering effects on inflammatory mediator C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)?
Study design:
This review article included 17 RCTs.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found coenzyme Q10 supplementation significantly reduced the levels of circulating CRP with 0.35 mg/L [95% CI = -0.64 to -0.05, p = 0.022].
The results of meta-regression showed that the changes of CRP were independent of baseline CRP, treatment duration, dosage and patients characteristics.
The investigators found coenzyme Q10 supplementation significantly reduced the levels of circulating IL-6 with 1.61 pg/mL [95% CI = -2.64 to -0.58, p = 0.002].
In the meta-regression analyses, a higher baseline IL-6 level was significantly associated with greater effects of coenzyme Q10 on IL-6 levels [p for interaction = 0.006].
The investigators found coenzyme Q10 supplementation significantly reduced the levels of circulating TNF-α with 0.49 pg/mL [95% CI = -0.93 to -0.06, p = 0.027].
The investigators concluded coenzyme Q10 supplementation has lowering effects on CRP, IL-6 and TNF-α. However, these results should be interpreted with caution because of evidence of heterogeneity between studies and limited number of studies.
Original title:
Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on inflammatory markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials by Fan L, Feng Y, […], Chen LH.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28179205
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find here more information/studies about coenzyme Q10.
Objectives:
Creatine is the most widely used supplementation to increase performance in strength; however, the most recent meta-analysis focused specifically on supplementation responses in muscles of the lower limbs without regard to upper limbs. Therefore, this review article (meta-analysis) has been conducted.
Does creatine supplementation increase strength performance of upper limb for exercise with a duration of less than 3 minutes?
Study design:
This review article included 53 studies (563 individuals in the creatine supplementation group and 575 individuals in the control group (placebo group)).
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found for creatine group versus control group no significant effect at T0. However, at T1, the effect size (ES) for bench press and chest press were 0.265 [95% CI = 0.132-0.398, p 0.001] and 0.677 [95% CI = 0.149-1.206, p = 0.012], respectively.
The investigators found for creatine group versus control group overall, pectoral ES was 0.289 [95% CI = 0.160-0.419, p = 0.000] and global upper limb ES was 0.317 [95% CI = 0.185-0.449, p 0.001].
The investigators found meta-analysis of changes between T0 and T1 gave similar results.
The investigators found meta-regression analysis showed no link with characteristics of population or supplementation, demonstrating the efficacy of creatine independently of all listed conditions.
The investigators concluded creatine supplementation is effective in upper limb strength performance for exercise with a duration of less than 3 minutes, independent of population characteristics, training protocols and supplementary doses or duration.
Original title:
Creatine Supplementation and Upper Limb Strength Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis by Lanhers C, Pereira B, […], Dutheil F.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27328852
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find here more information/studies about sport nutrition and creatine.
Objectives:
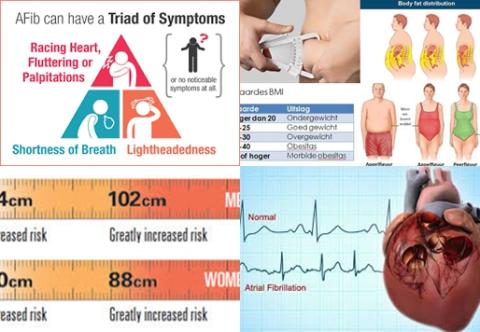
Different adiposity measures have been associated with increased risk of atrial fibrillation, however, results have previously only been summarized for BMI. Therefore, this review article (meta-analysis) has been conducted.
Is there an association between different adiposity measures and risk of atrial fibrillation?
Study design:
This review article included 25 prospective studies with 83,006 cases among 2,405,381 participants.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found every 5 unit increment in BMI significantly increased risk of atrial fibrillation with 28% [RR= 1.28, 95% CI = 1.20-1.38, I2 = 97%].
The investigators found every 10 cm increase in waist circumference significantly increased risk of atrial fibrillation with 18% [95% CI = 1.12-1.25, I2 = 73%, n = 5].
The investigators found every 10 cm increase in hip circumference significantly increased risk of atrial fibrillation with 32% [95% CI = 1.16-1.51, I2 = 91%, n = 3].
The investigators found every 0.1 unit increase in waist-to-hip ratio significantly increased risk of atrial fibrillation with 9% [95% CI = 1.02-1.16, I2 = 44%, n = 4].
The investigators found every 5 kg increase in fat mass significantly increased risk of atrial fibrillation with 9% [95% CI = 1.02-1.16, I2 = 94%, n = 4].
The investigators found every 10% increase in fat percentage nonsignificantly increased risk of atrial fibrillation with 10% [95% CI = 0.92-1.33, I2 = 90%, n = 3]. Nonsignificantly because RR of 1 can be found in the 95% CI of 0.92 to 1.33. RR of 1 means no risk.
The investigators found every 5 kg increase in weight significantly increased risk of atrial fibrillation with 10% [95% CI = 1.08-1.13, I2 = 74%, n = 10].
The investigators found every 5% increase in weight gain nonsignificantly increased risk of atrial fibrillation with 8% [95% CI = 0.97-1.19, I2 = 86%, n = 2]. Nonsignificantly means, there is no association at a 95% confidence.
The investigators found the association between BMI and atrial fibrillation was nonlinear [p nonlinearity 0.0001] with a stronger association at higher BMI levels. However, increased risk was observed even at a BMI of 22-24 compared to 20.
The investigators concluded general and abdominal adiposity and higher body fat mass increase risk of atrial fibrillation.
Original title:
Body mass index, abdominal fatness, fat mass and the risk of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies by Aune D, Sen A, […], Vatten LJ.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28194602
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find here more information/studies about cardiovascular diseases and overweight.

Objectives:
The associations between dietary zinc and iron intake and risk of depression remain controversial. Therefore, this meta-analysis (systematic review) has been conducted.
Do dietary zink and iron intake decrease risk of depression?
Study design:
This review article included a total of 9 studies for dietary zinc intake and 3 studies for dietary iron intake.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found for the highest versus lowest dietary zinc a significant reduced risk of 33% [pooled RR = 0.67, 95% CI = 0.58-0.76] for depression.
The investigators found for the highest versus lowest dietary iron a significant reduced risk of 43% [pooled RR = 0.57, 95% CI = 0.34-0.95] for depression.
The investigators found in subgroup analysis by study design, the inverse association between dietary zinc intake and risk of depression remained significant in cohort studies and cross-sectional studies.
The investigators found the pooled RRs (95% CIs) for depression did not substantially change in the influence analysis and subgroup analysis by adjustment for body mass index (BMI).
The investigators concluded dietary zinc intake reduces risk of depression.
Original title:
Dietary zinc and iron intake and risk of depression: A meta-analysis by Li Z, Li B, [...], Zhang D.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28189077
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find here more information/studies about zinc and review article/95% CI.
Objectives:
Vitamin B12 deficiency in pregnancy is prevalent and has been associated with both lower birth weight (birth weight 2,500 g) and preterm birth (length of gestation 37 weeks). Nevertheless, current evidence is contradictory. Therefore, this meta-analysis (systematic review) has been conducted.
Is there an association between maternal serum or plasma vitamin B12 concentrations in pregnancy and offspring birth weight and length of gestation?
Study design:
This review article included 18 studies.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found a non-linear association between maternal vitamin B12 levels in pregnancy and birth weight.
The investigators found vitamin B12 deficiency (148 pmol/L) was significantly associated with a 15% higher risk for low birth weight in newborns [adjusted risk ratio = 1.15, 95% CI = 1.01 to 1.31].
The investigators found for each 1-standard-deviation increase in maternal levels of vitamin B12 a significant reduced risk of 11% for preterm birth [adjusted risk ratio = 0.89, 95% CI = 0.82 to 0.97].
The investigators found vitamin B12 deficiency (148 pmol/L) was non-significantly associated with a 21% higher risk for preterm birth [adjusted risk ratio = 1.21, 95% CI = 0.99 to 1.49].
The investigators concluded a maternal vitamin B12 deficiency (148 pmol/L) was associated with a higher risk for low birth weight in newborns. Therefore, this finding supports the need for randomized controlled trials of vitamin B12 supplementation in pregnancy.
Original title:
Associations of Maternal Vitamin B12 Concentration in Pregnancy With the Risks of Preterm Birth and Low Birth Weight: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Individual Participant Data by Rogne T, Tielemans MJ, [...], Risnes KR.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28108470
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find here more information/studies about vitamin B12 and pregnancy.
Objectives:
Arthritis patients often take fish oil supplements to alleviate symptoms, but limited evidence exists regarding their efficacy. Therefore, this meta-analysis (systematic review) has been conducted.
Do taking marine oil supplements alleviate pain in arthritis patients?
Study design:
This review article included 42 randomized trials; 30 trials reported complete data on pain.
The trials used treatment durations from 2 weeks to 18 months, with doses of EPA from 0.013 to 4.050 g/day and doses of DHA from 0.010 to 2.700 g/day.
Most trials used marine oil from whole fish, but some used cod liver oil, mussel extracts, seal oil and krill oil.
The trials included 2751 patients with a mean age of 53.8 years (range of mean age of 10-68 years) and the mean disease duration was 9.7 years (range 2.3-19.0 years).
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found a favorable effect [SMD = -0.24, 95% CI = -0.42 to -0.07, I2 = 63%] for using marine oil supplements.
The investigators found in 22 trials a significant effect in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [SMD = -0.21, 95% CI = -0.42 to -0.004] for using marine oil supplements.
The investigators also found in 3 trials a significant effect for other or mixed diagnoses [SMD = -0.63, 95% CI = -1.20 to -0.06] for using marine oil supplements, but no significant effect was found in osteoarthritis patients [5 trials: SMD = -0.17, 95% CI = -0.57 to 0.24].
The investigators found a significant, beneficial effect on pain for marine oil with an EPA/DHA ratio >1.5.
The investigators found a significant positive association between SMD and total dose of EPA and DHA [slope β, 0.13 (g/day), 95% CI = 0.04 to 0.22, p = 0.006], indicating less effect at higher dose, but there was no duration-response relationship [p = 0.568].
The investigators concluded using marine oil supplements (with an EPA/DHA ratio >1.5) alleviates pain in rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Original title:
Marine Oil Supplements for Arthritis Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials by Senftleber NK, Nielsen SM, […], Christensen R.
Link:
http://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/9/1/42/htm
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find here more information/studies about EPA&DHA and chronic diseases.

Objectives:
The role of vitamin D status in the etiology of allergic diseases is uncertain. Therefore, this meta-analysis (systematic review) has been conducted.
Study design:
This review article included a total of 21 observational studies.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found children with serum 25(OH)D ≥75 nmol/L had significantly reduced odds of aeroallergen sensitization, but neither vitamin D intake during pregnancy nor vitamin D supplementation in infancy were associated with risk of allergic rhinitis.
The investigators found compared to those with serum 25(OH)D 50 nmol/L, individuals with serum 25(OH)D ≥75 nmol/L had a significant decreased risk of 29% [OR = 0.71, 95% CI = 0.56-0.89, p = 0.04] for allergic rhinitis.
However, this association was mainly observed in adult men; prevalence of allergic rhinitis (AR) was lower in men with serum 25(OH)D ≥75 nmol/L compared to men with serum 25(OH)D 50 nmol/L, while this association was not observed in women.
The investigators concluded serum 25(OH)D ≥75 nmol/L reduced odds of aeroallergen sensitization in children and risk of allergic rhinitis in men.
Original title:
Vitamin D status, aeroallergen sensitization, and allergic rhinitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis by Aryan Z, Rezaei N and Camargo CA Jr.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28102718
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find here more information/studies about vitamin D and chronic diseases.

Objectives:
Data on the longitudinal association of walking pace with the risk of cognitive decline and dementia are inconsistent and inconclusive. Therefore, this meta-analysis (review) of prospective cohort studies has been conducted.
Does walking pace reduce risk of cognitive decline or dementia in elderly populations?
Study design:
This review article included 17 prospective cohort studies, including 10 studies reporting the RR of cognitive decline (9,949 participants and 2,547 events) and 10 presenting the RR of dementia (14,140 participants and 1,903 events).
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found for the lowest comparing to the highest category of walking pace, a significant increased risk of 89% [pooled RR = 1.89, 95% CI = 1.54-2.31] for cognitive decline in elderly populations.
The investigators found for the lowest comparing to the highest category of walking pace, a significant increased risk of 66% [pooled RR = 1.66, 95% CI = 1.43-1.92] for dementia in elderly populations.
The investigators found with every 1 dm/s (360 m/h) decrement in walking pace, the risk of dementia was significantly increased by 13% [RR = 1.13, 95% CI = 1.08-1.18].
The investigators concluded that slow or decreased walking pace is associated with elevated risk of cognitive decline and dementia in elderly populations.
Original title:
Walking Pace and the Risk of Cognitive Decline and Dementia in Elderly Populations: A Meta-analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies by Quan M, Xun P, [...], He K.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27927757
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find here more information/studies about elderly and sport nutrition.
According to WHO in order to improve cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness, bone and functional health, reduce the risk of NCDs, depression and cognitive decline:
Objectives:
Do consuming tomato products and lycopene supplementation reduce cardiovascular risk among adult subjects >18 years of age?
Study design:
This review article included 21 studies.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found consuming tomato was associated with a significant reduction of 0.22 mmol/L in LDL-cholesterol [p = 0.006]. Significant means, there is an association at a 95% confidence.
The investigators found consuming tomato was associated with a significant reduction of 0.25 in plasma IL-6 concentration [p = 0.03].
The investigators found consuming tomato was associated with a significant improvement of 2.53% in flow-mediated dilation (FMD) [p = 0.01].
The investigators found lycopene supplementation reduced systolic blood pressure with 5.66 mmHg [p = 0.002].
The investigators found no other outcome was significantly affected by these interventions.
The investigators concluded consuming tomato products and lycopene supplementation had positive effects on blood lipids, blood pressure and endothelial function. These results support the development of promising individualised nutritional strategies involving tomatoes to tackle cardiovascular diseases.
Original title:
Tomato and lycopene supplementation and cardiovascular risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis by Cheng HM, Koutsidis G, […], Lara J.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28129549
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find here more information/studies about vegetable consumption, carotenoids and cardiovascular diseases.
Impaired endothelial function is an early indicator of atherosclerosis. Endothelial function is often quantified by flow-mediated dilation (FMD), which represents the endothelium-dependent relaxation of a conduit artery-typically the brachial artery - due to an increased blood flow. Flow-mediated dilation (FMD) is endothelium-dependent and can be assessed by ultrasound in the brachial artery.