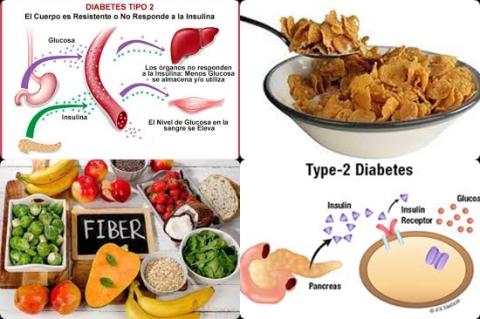
Moderate plant protein decreases type 2 diabetes mellitus

Objectives:
Dietary proteins, including those obtained from animal and plant sources, have inconsistently been correlated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) risk. Therefore, this review article (meta-analysis) has been conducted.
Does dietary protein intake increase risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Study design:
This review article included 21 cohort studies with a total of 487,956 individuals and 38,350 T2DM cases (persons with type 2 diabetes mellitus).
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found high total dietary protein intake was associated with an increased risk of 10% for type 2 diabetes mellitus [RR = 1.10, p = 0.006] whereas moderate total dietary protein intake was not significantly associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus risk [RR = 1.00, p = 0.917].
Not significantly because the calculated p-value of 0.917 was larger than the p-value of 0.05.
The investigators found, moreover, an increased risk of 13% [RR = 1.13, p = 0.013] for type 2 diabetes mellitus was observed with high dietary animal protein intake whereas moderate animal protein intake had little or no effect on type 2 diabetes mellitus risk [RR = 1.06, p = 0.058].
The investigators found, high dietary intake of plant protein did not affect type 2 diabetes mellitus risk [RR = 0.93, p = 0.074], whereas moderate intake was associated with a reduced risk of 6% for type 2 diabetes mellitus [RR = 0.94, p 0.001].
The investigators concluded high dietary total protein and dietary animal protein intakes are associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus, whereas moderate plant protein intake is associated with a decreased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Original title:
Dietary protein intake and subsequent risk of type 2 diabetes: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies by Ye J, Yu Q, [...], Wang Y.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30929078
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on diabetes and protein right here.
A diet with high protein intake is a diet with a minimum of 35 En% protein (En% = energy percentage). These products from the supermarket contain at least 35 En% protein.
35 En% protein means that the amounts of protein contribute 35% to the total calories (kcal) of the diet.
If the diet contains 2000 kcal, 175 grams of protein contribute 35% to this 2000 kcal.
1 gram of protein gives 4 kcal. Thus, 175 grams of protein provide 700 kcal and 700 kcal is 35% of 2000 kcal.
A diet with moderate protein consumption is a diet with 20-25 En% protein. The easiest way to follow a diet with moderate protein consumption is to choose only products/meals that also contain 20-25 En% protein. These products from the supermarket contain 20-25 En% protein.